Respiratory diseases: H9 control in mutual conspiracy

The poultry industry, particularly broiler production, is vital for global food security, facing persistent challenges in the Middle East and North Africa due to respiratory diseases, notably avian influenza H9N2. This subtype causes significant economic losses and increased mortality in broilers. This review addresses the current situation and impact of H9N2 avian influenza, emphasising the crucial role of biosecurity and farm management (Part I), exploring the concept of mutual conspiracy (Part II), and discussing targeted control through vaccination (Part III), with a focus on the Newflend vaccine.
Biosecurity and farm management
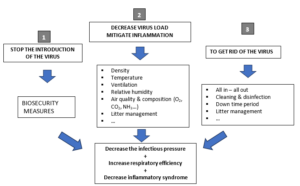
Respiratory diseases, including H9N2 avian influenza, require stringent biosecurity measures to prevent infection and spread. A continuous improvement process should address areas like viral colonisation prevention through audits. Effective farm management strategies, such as temperature control, air quality, and litter management, play a vital role in reducing infectious pressure.
Figure 1- Key points of biosecurity & management in preventing respiratory diseases.
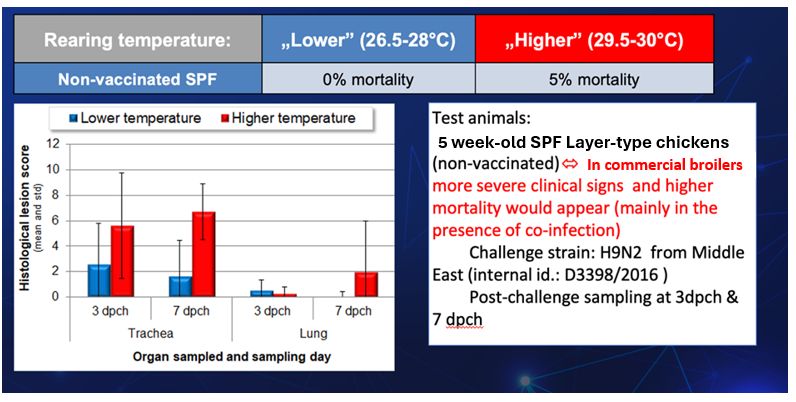
Temperature Control: Research reveals temperature-dependent fluctuations in H9N2 pathogenicity, emphasising the importance of maintaining optimal rearing temperatures.
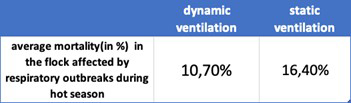
Air Quality: Poor air quality exacerbates respiratory infections, making birds more susceptible. Proper ventilation is crucial to obtain good oxygenation, and dynamic systems significantly reduce pathogen prevalence.
Relative Humidity and Litter Management: Maintaining appropriate humidity levels and effective litter management is crucial in controlling respiratory diseases. Well-managed litter minimises pathogen proliferation, reducing the risk of respiratory infectious diseases.
Density and Micro-Climate Impact: Poultry density influences micro-climate, affecting bird health. Managing flock density is crucial for maintaining suitable air quality, proper oxygenation, and optimal animal health.
Figure 2- Effect of rearing conditions on the outcome of H9 challenge.
Mutual conspiracy
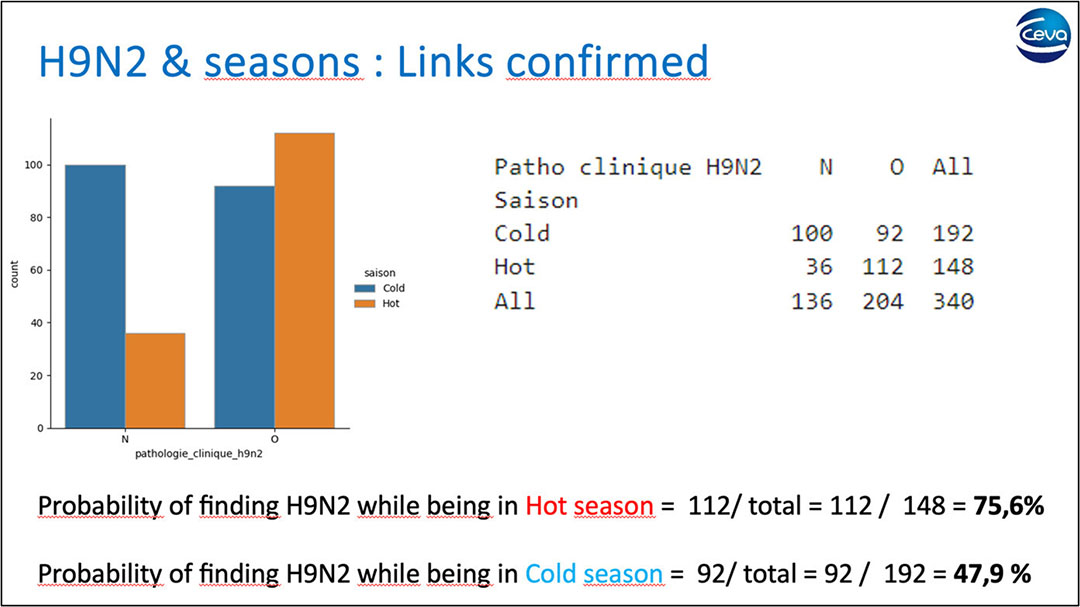
The term “mutual conspiracy” describes the synergistic interaction of pathogens like H9N2 with others, amplifying the challenge of disease control. Field data supports the hypothesis that higher ambient temperatures increase vulnerability to respiratory disease outbreaks, emphasising the practical implications of managing temperature.
Figure 3 – Reproduction of the macroscopic & histological lesions of the co-infection H9 & IBV but with a stand alone H9N2 challenge (+lower ventilation and higher temperature).
Vaccination with Newflend
The Newflend vaccine marks a milestone in H9N2 immunisation, providing an innovative approach to managing H9 and addressing mutual conspiracy complexities. Its unique concept offers a new mechanism in respiratory disease control, successfully tackling the dual challenge of H9N2 and other respiratory pathogens.
Conclusion
Effective biosecurity and strategic farm management are critical in protecting broilers against respiratory diseases’ mutual conspiracy. Understanding the interplay of factors like temperature, air quality, and density, along with the introduction of innovative vaccines like Newflend, is essential for sustainable broiler production, mitigating economic losses, and ensuring global food security.
References available upon request.






